文章题目:
Learning representations of microbe–metabolite interactions
文章Supplementary
这篇文章中的interactions across omics就是指在统计学意义上的两个变量的关系,如相关性.
microbe-metabolite relationship就是指微生物和metabolite的相关性.
1 Abstract
Previous work has been able to predict metabolite abundance profiles from microbe abundance profiles1 2. However, because conventional correlation techniques have unacceptably high false-discovery rates, finding meaningful relationships between genes within complex microbiomes and their products in the metabolome is challenging.
传统的correlation计算方法有着非常大的错误发现率,因此发现microbe和他们的product metabolite还是非常具有挑战性的.
Relative abundances of thousands of microbes and metabolites can be measured using sequencing technology and mass spectrometry, respectively, resulting in the generation of high-dimensional microbiome and metabolomics datasets.
microbiome得到的定量信息也是relative abundance.对于metabolome数据,能够测到的metabolite依赖于提取的方法以及分析方法,因此其实我们得到的metabolome是a partial snapshot of the metabolome.并不完全的完整的.
Quantifying microbe–metabolite interactions from these abundances requires estimating a distribution across all possible microbe–metabolite interactions.
从相对定量的数据中得到microbe-metabolite interactions需要得到所有的microbe–metabolite interactions的分布.是否可以理解为需要由NULL分布,然后才能知道某个interaction是不是真的interaction?
Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlations assume independence between interactions.
我们常用的correlation方法假设两个变量之间的关系和其他的变量是独立的,这是不一定的.所以还有一种办法叫做偏相关性.
作者举了例子来说明,为什么使用传统的correlation数据会早成错误发现(假阳性或者假阴性).
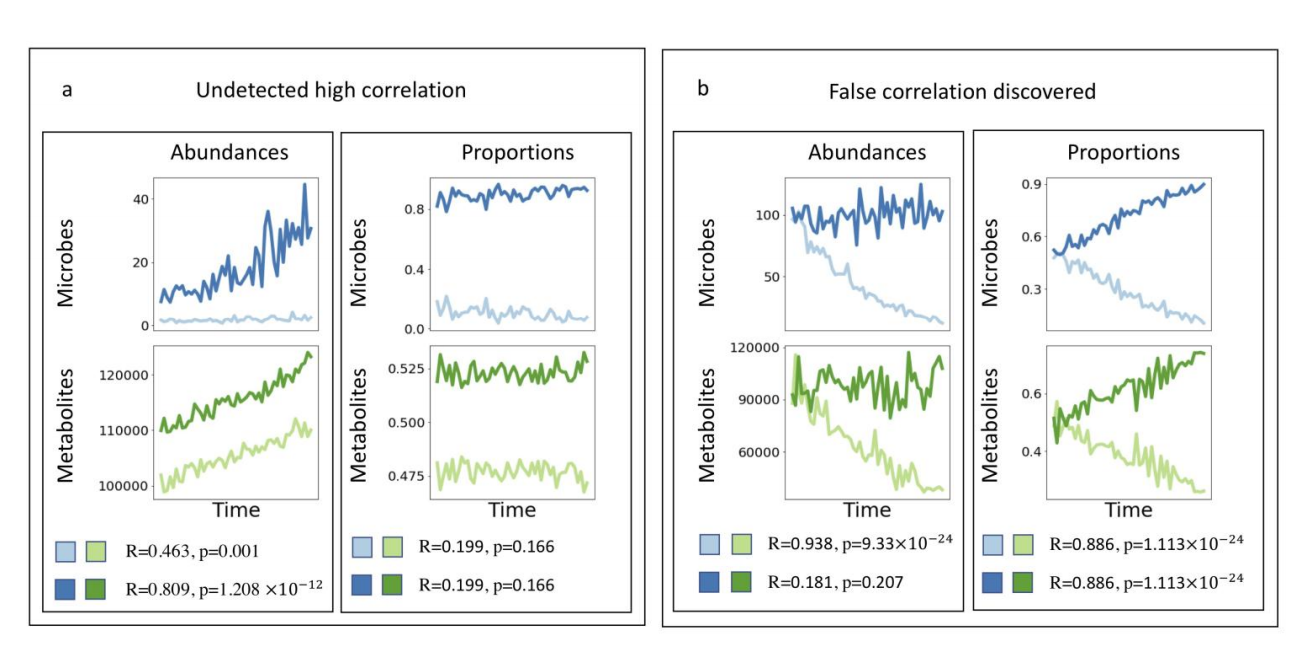
Supplementary Figure 1
我并没有看懂他是什么意思?
在microbome和metabolite中会有使用某个变量占所有变量的比例来表示这个变量的吗?
好像并没有啊.
scale invariance什么意思?标度不变.
An alternative approach is to consider co-occurrence probabilities instead of correlations.
一个可替代的方法是考虑共出现的概率而不是相关性.
Here, co-occurrence probabilities refer to the conditional probability of observing a metabolite given that a microbe was observed, thereby allowing us to identify the most likely microbe–metabolite interactions.
共出现概率是指当一个microbe(细菌)在的时候,观察到某个代谢物的条件概率.从而能够鉴定到真正的microbe-metabolite interaction.
To do this, we propose ‘mmvec’, (microbe–metabolite vecors), a neural network that predicts an entire metabolite abundance profile from a single microbe sequence.
因此作者提出了mmvec(microbe–metabolite vecors)概念.利用neural network从一个single microbe的sequence来预测整个的metabolite abundance.
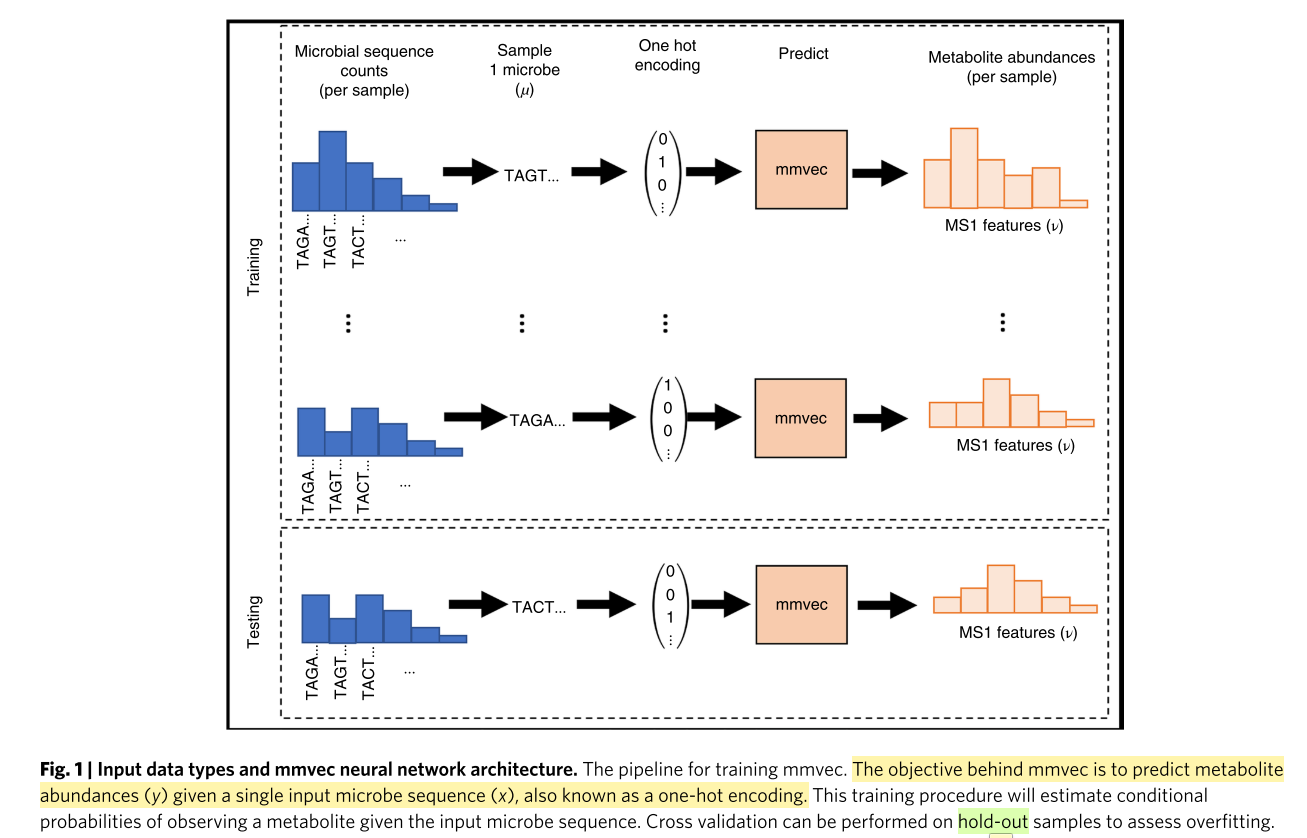
Figure 1
这幅图是指如何使用microbe sequence去预测metabolite abundance.
Through iterative training, mmvec can learn the co-occurrence probabilities between microbes and metabolites. The microbe–metabolite interactions can be ranked and visualized through standard dimensionality reduction interfaces, enabling interpretable findings.
其实就是给定microbe的中的一个sequnce之后,预测所有metabolite abundance.
2 Results
3 Reference
Noecker, C. et al. Metabolic model-based integration of microbiome taxonomic and metabolomic profiles elucidates mechanistic links between ecological and metabolic variation. MSystems 1, e00013–e00015 (2016).↩︎
Mallick, H. et al. Predictive metabolomic profiling of microbial communities using amplicon or metagenomic sequences. Nat. Commun. 10, 3136 (2019).↩︎