1 文献题目:
Noninvasive blood tests for fetal development predict gestational age and preterm delivery
2 Summary
Noninvasive blood tests that provide information about fetal development and gestational age could potentially improve prenatal care. Ultrasound, the current gold standard, is not always affordable in low-resource settings and does not predict spontaneous preterm birth, a leading cause of infant death. In a pilot study of 31 healthy pregnant women, we found that measurement of nine cell-free RNA (cfRNA) transcripts in maternal blood predicted gestational age with comparable accuracy to ultrasound but at substantially lower cost. In a related study of 38 women (25 full-term and 13 preterm deliveries), all at elevated risk of delivering preterm, we identified seven cfRNA transcripts that accurately classified women who delivered preterm up to 2 months in advance of labor. These tests hold promise for prenatal care in both the developed and developing worlds, although they require validation in larger, blinded clinical trials.
2.1 Results
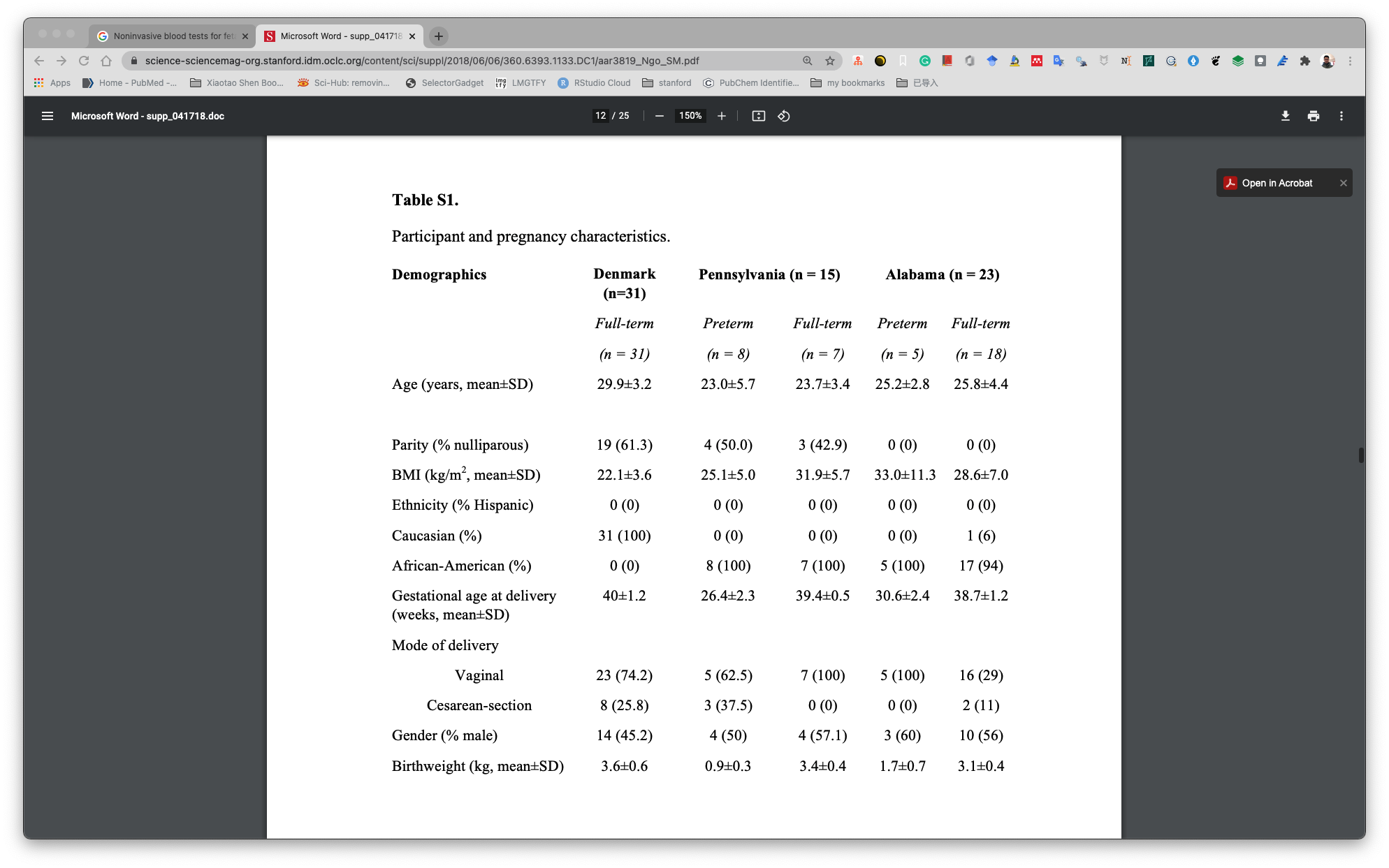
31个pregnant women,mothly sampling.共有521个plasma samples.所有women都是full term (delivery GA >= 37 weeks).记录了medicine. 强调了:
and their medical records showed no unusual health changes during pregnancy (table S1).
但是table S1中并没有记录.
测cfRNA时,特异性的只测量某些:
Each sam- ple was analyzed by highlymultiplexed real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a panel of genes with expression specific to the placenta or to the immune system, or highly enriched in the fetal liver (table S2).
某些placental(胎盘)cfRNA在delivery之后就无法测量到.
Placental cfRNAs and several fetal liver cfRNAs were not detected above the noise floor after delivery, which sup- ports their pregnancy-derived origin; some fetal liver transcripts were also expressed in the adult liver, and we observed a small maternal baseline for this subset. cfRNAmeasurements
跟immune system相关的cfRNA在GA期间逐渐升高,然后delivery之后恢复到正常水平,说明在GA期间主要是有怀孕引起的升高.
cfRNAmeasurements correspond- ing to immune system–related genes increased during gestation and showed a return to measurable baselines after delivery, which supports their predominantly maternal origin.
BMI并不影响到cfRNA的含量.将women分为几组,然后使用wulcoxon test检验.
We have tested for the effect of BMI on circulating cfRNA levels using estimated transcript counts of GAPDH per milliliter of plasma and found no significant difference between underweight (BMI < 18.5), normal weight (18.5 ≤ BMI < 25), overweight (25 ≤ BMI < 30), and obese (BMI ≥ 30) individuals both before and after Bonferroni correction using a Wilcoxon rank sum test.
P-values for distinct tests of GAPDH levels before and after Bonferroni correction, respectively, were as follows: (1) underweight versus normal weight (P = 0.58, 1), underweight versus overweight (P = 0.12, 0.80), underweight versus obese (P = 0.26, 1), normal weight versus overweight (P = 0.06, 0.35), normal weight versus obese (P = 0.16, 0.95), and overweight versus obese (P = 0.72, 1). Similar results were obtained for placental-specific cfRNAs such as CAPN6, CGA, and CGB.
All comparisons were done within cohorts so that differences in BMI distribution between cohorts were not confounding.
建立预测GA模型,使用了RF模型,徐哪去最后九个cfRNA作为maker.预测效果跟使用所有51个cfRNA相差无几.预测效果随着GA增加而变好.third trimester效果最好.
We then built a random forest model to predict time from sample collection until delivery, using cfRNA measurements as the primary fea- tures. We also found that model performance improved significantly over the course of pregnancy, as measured by root mean squared error (RMSE) for both training [RMSE = 6.0 (first trimester, T1), 3.9 (second trimester, T2), 3.3 (third trimester, T3), 3.7 (postpartum, PP) weeks] (Fig. 2C) and validation sets [RMSE = 5.4 (T1), 4.2 (T2), 3.8 (T3), 2.6 (PP) weeks] (Fig. 2D). Although